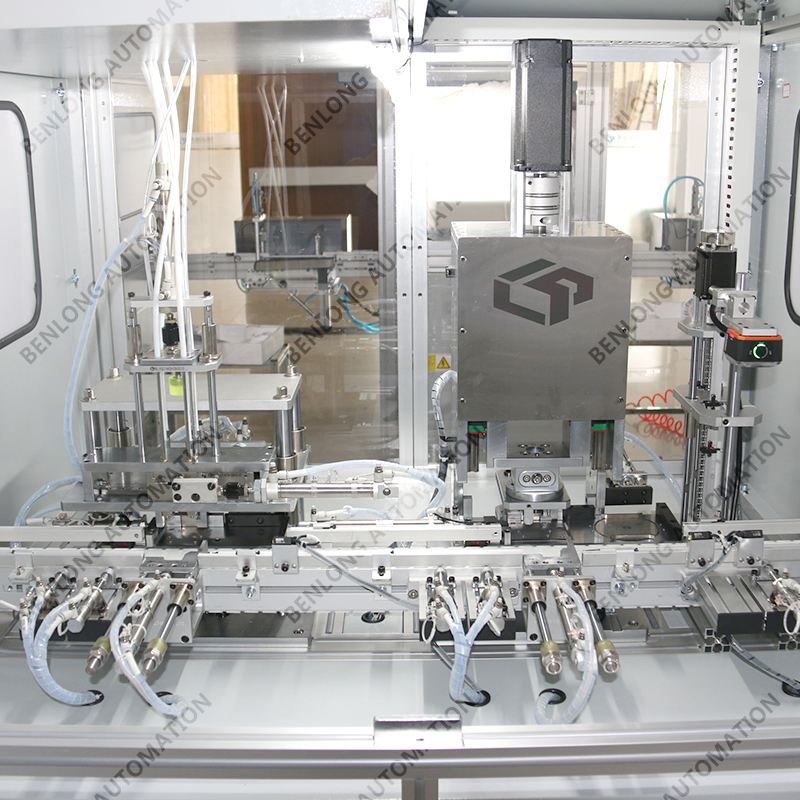
MCB Automatic Pin Insertion and Riveting Machine
See More>>Process Flow of MCB Automatic Riveting Machine
Ⅰ. Parts Feeding
· MCB housings, copper conductors, and contact pieces are automatically fed by vibratorybowl feeders or robotic arms.
· Workpieces are transferred to the workstation and clamped in precise positioning jigs.
Ⅱ. Rivet Feeding
· Rivets are oriented and sorted through a vibratory feeder.
· They are delivered to the riveting station via a feeding track or pipe.
Ⅲ. Rivet Insertion
· A pneumatic cylinder or servo-driven unit inserts the rivet into the reserved hole of theMCB housing and conductor assembly.
· The jig ensures accurate alignment during insertion.
Ⅳ. Riveting Forming
· The riveting head (pneumatic, hydraulic, or servo type) presses down to deform the rivettail, achieving a firm mechanical connection.
· Force and displacement sensors monitor the riveting process to ensure quality.
V. Quality Inspection
· Vision sensors or displacement detectors check for missing rivets, misalignment, orincomplete riveting.
· Defective parts are automatically rejected.
Ⅵ. Workpiece Transfer
· Finished MCB assemblies are conveyed to the next process station, such as sealing capassembly, trip mechanism installation, or functional testing.
MCB Automatic Pin Insertion and Riveting Machine